Ethics
Relevant, tagged site content:
Engagement Activities
Vector is an immersive theatre experience that tasks participants with ethically reviewing the use of animal models in vaccine development.
Publications
Two Worlds in One: What ‘Counts’ as Animal Advocacy for Veterinarians Working in UK Animal Research?
The concept of advocacy is of increasing importance to the veterinary profession internationally. However, there are concerns around the ambiguity and complexity of acting as an advocate in practice.
The veterinary profession has been relatively understudied in social science, though recent work has highlighted the geographic dimensions of veterinary expertise.
In the UK, claims are often made that public support for animal research is stronger when such use is categorised as for medical purposes. Drawing on a qualitative analysis of writing from the Mass Observation Project, a national writing project documenting everyday life in Britain, this paper suggests that the necessity of using animals for medical research is not a given but understood relationally through interactions with inherent vulnerability. This paper stresses the ubiquity of ambivalence towards uses of animals for medical research, complicating what is meant by claims that such use is ‘acceptable’, and suggests that science-society dialogues on animal research should accommodate different modes of thinking about health. In demonstrating how understandings of health are bound up with ethical obligations to care for both human and non-human others, this paper reinforces the importance of interspecies relations in health and illness and in the socio-ethical dimensions of biomedicine.
This paper explores what happens to care, and decisions about ending and extending life, when research animals become pets and pets become research animals. To do this, we draw on in- depth qualitative research on (i) rehoming of laboratory animals, (ii) veterinary clinical research, and (iii) the role of the Named Veterinary Surgeon (NVS) in UK animal research. Key contributions of our work include highlighting: how care roles can be split; the impor- tance of considering speculative and in-practice elements of care; the context-dependency and multiplicity of practices of killing in the veterinary clinic and laboratory; and the flexibility and changing nature of animal categories.
This thesis, written by Tess Skidmore, explores the rehoming of laboratory animals. Drawing on qualitative interviews and a semi-structured questionnaire, the thesis investigates the sociocultural and political importance of the growing attention toward rehoming.
Drawing on insights from qualitative social science research, this paper aims to prompt reflection on social, ethical and regulatory challenges faced by scientists undertaking invasive animal research in the field. We explore challenges relating to the management of (i) relationships with publics and stakeholders; (ii) ethical considerations not present in the laboratory; (iii) working under an array of regulations; and (iv) relationships with regulators (especially vets). We argue that flexibility—at a personal and policy level—and respect for others’ expertise emerged as two key ways of negotiating ethical challenges, fostering positive working relationships and promoting good care for individual animals and broader ecosystems.
Laboratory animal science represents a challenging and controversial form of human-animal relations because its practice involves the deliberate and inadvertent harming and killing of animals. We propose that different notions of care are enacted alongside, not only permitted levels of harm inflicted on research animals following research protocols, but also harms to ATs in the processes of caring and killing animals.
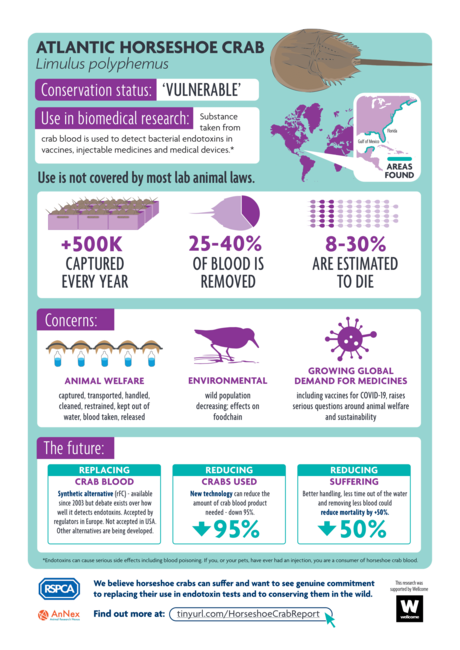
Rich Gorman’s secondment to the RSPCA explored the social relations shaping the use of horseshoe crab blood within pharmaceutical endotoxin testing. This involved 13 stakeholder interviews, and has resulted in a stakeholder report alongside a peer-reviewed journal publication. Rich has also presented the research at industry conferences and academic seminars. This is the report and infographic produced for his research.
Animal research conducted outside of the laboratory faces various unique challenges, but has received only limited attention in terms of official guidelines, support, and statistics.
Citizen science involves participation by members of the public in scientific research. In wildlife research, citizen scientists might be involved in the capture and handling of animals (e.g.
While sociologists of medicine have focused their efforts on understanding human health, illness, and medicine, veterinary medical practice has not yet caught their attention in any sustained way. In this critical review article, we use insights from the sociology of diagnosis literature to explore veterinary practice, and aim to demonstrate the importance of animals to sociological understandings of health, illness and disease. We hope that this work encourages more focus on the veterinary profession, and a better understanding of the role of the vet inside and outside the laboratory.
The issues of openness, transparency and public engagement about animal research have taken focus in several different countries in recent years. This open access paper gives an account of a two-day-long, international expert forum on this topic.
This Statement explains how the Animal Research Nexus Team makes use of any personal information collected about you in connection with our research.
In our experience so far, one aspect of working collaboratively is that tacit assumptions about academic working practices need to be made explicit. This report aims to highlight our working assumptions about the topic of publication ethics.
This paper draws on ethnographic work with laboratory animal technologists to offer insights into the skills required to study human–animal relations and the role played by storytelling in negotiating the contested moral economies of animal research.
The Routledge Companion to Animal-Human History provides an up-to-date guide for the historian working within the growing field of animal-human history. This book chapter by Rob Kirk suggests that to understand animal–human history we would do well to start with the role of animals in science.
Vets play an important role in a wide variety of social contexts, including in ‘non-therapeutic’ roles, for example in facilitating the use of animals in sport or for food production. This paper focuses on a further non-therapeutic example, namely the role of the vet in laboratory animal research
Blog entry
Over three days in July 2022, colleagues from the UK and beyond gathered online to discuss the thorny question of veterinary expertise.
In part 1 of this blog series, we introduced the idea of a ‘spectrum of visibility’ in animal research, with
In my PhD work on societal views towards animal research, I’ve found that the area of cosmetics is often held up as an unambiguous example of the ethical limits of using animals in science, with cosmetic products and procedures providing an easy m
The COVID-19 crisis has clearly had significant effects on animal research, including research in the field.
Social scientists and historians have long observed that laboratory and field research are rather different (e.g., Gieryn, 2006; Kohler, 2002).
Can animals volunteer to participate in research? If so, what does volunteering look like, and what does it mean for animal welfare?
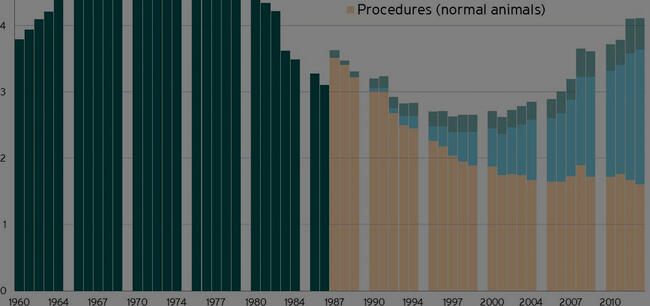
Numbers can be a contentious issue in animal research.
In the Species and Spaces project, we’re exploring people’s perceptions around fish use, sentience, and how these shape and define assumptions around their welfare requirements.
Understanding and examining the significance of the laboratory space physically, practically, emotionally and metaphorically, is opening up new lines of social scientific enquiry regarding the relations between health, science and welfare
"How different does a fish really feel from one day to the next?" Zebrafish larvae become protected animals at the age of 5 days post fertilisation. At 4 days, they are not. Why is this?
Working within a multidisciplinary research environment provides every member of the AnNex team with unique opportunities to think outside the boundaries of their own discipline and benefit from exposure to the methods and perspectives of other hu
Animal research can be a controversial issue. It involves complex questions across science, health, animal welfare, and ethics and is the subject of ongoing social and scientific debate.
In June 2018, several members of AnNex flew to the beautiful city of Vienna to take part in the 14th Congress of the European Society for Agricultural and Food Ethics (EurSafe) with a workshop on animal resear
Events
Academics at the University of Nottingham are pleased to announce that a conference on Veterinary Expertise is now available for booking!
What kinds of ethical and practical challenges do wildlife researchers face? How do these challenges compare with those faced by researchers working with laboratory animals?
For many, talking about animal research remains taboo. As a way of highlighting one of the roles that animal research plays, some have suggested labelling medicines as ‘tested on animals’. But is the act of labelling so simple?
Where do lab mice come from? Where do they end up? Joins us for crafting felt mice to exchange or take home. You can also explore the history, practices, and ideas of care involved in making laboratory mice.
Where do lab mice come from? Where do they end up? Joins us for crafting felt mice to exchange or take home. You can also explore the history, practices, and ideas of care involved in making laboratory mice.
Join researchers from the University of Southampton for a family day suitable for all ages.
Oxford University’s first Open Doors Community Fair, taking place in the Weston Library’s stunning Blackwell Hall in Broad Street on Saturday 10 September between 1pm and 4pm.
Take part in live experiments, chat to scientists and get hands-on with innovative activities based on cutting edge research in science, technology, engineering and maths.
Venue:
Friday 28 September is European Researcher’s night, and for the fourth time Manchester Museum will be hosting Science Uncovered Manchester - a special late opening showcasing Manchester’s finest researchers and their work for an adult audience.
Announcements
The University of Nottingham as part of Midlands Graduate School is now inviting applications for an ESRC Doctoral Studentship in association with our collaborative partner, RSPCA, to commence in October 2019.